Managing Trust Ledger Accounts
The different types of accounts that are available in the assets and liabilities ledger
This article describes the different types of accounts that are available in the assets and liabilities ledger and a brief overview of their uses and how to edit them.
Contents
What is an account?
In the context of a trust ledger, an account is a repository that funds may move into or out of. In this sense, an account may be:
-
A bank account out of which the trust makes payments, or into which the trust receives income.
-
A loan account, recording a loan the trust has received from a bank or other party.
-
A distribution account records the distributions that have been made to a particular beneficiary.
-
A non-current asset, like a house, boat, or other trust property. These are treated as accounts into which funds of the trust have been moved.
-
An income or expense category allows all income or expenses relating to a particular source to be tracked.
-
A suspense account, for recording any trust funds that have not been allocated to another account.
The Chart of Accounts tab displays all accounts that have been created for the trust. Accounts are grouped into categories, which you can then use as filters to review specific account types (eg. expenses or distributions).
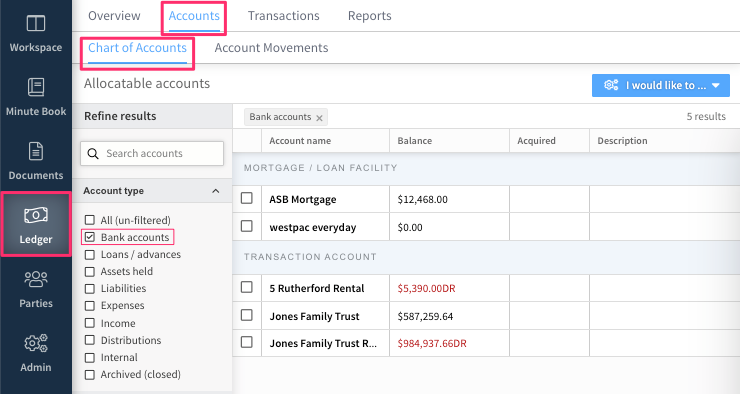
When funds are moved into an account, the balance of the account increases. When funds are moved out of an account, the balance of the account decreases. Accounts with a negative or overdrawn balance have their balance displayed in red.
Types of account
Bank accounts:
-
Mortgage/debt account - Use to record a mortgage or other loan from a bank, and to track repayments of bank loans. This account type is recorded as a liability.
-
Trading/transaction account - Use to record balances, payments, receipts, or transfer of funds into or out of a trading or transaction bank account. This account type is recorded as an asset.
-
Savings account - Use to record payments, receipts, or transfers of funds into or out of a savings bank account. This account type is recorded as an asset.
-
Other bank (liability) account - Use to record any other bank transactions that are not captured by the previous account types. This account type is recorded as a liability.
-
Credit Card account - Use to record expenditures against a trust’s credit card(s) or repayment of credit card debt.
General accounts:
-
Loan (non-bank) account - use to record a loan from a non-bank third party, such as the trust's settlors. This account type is recorded as a liability.
-
Current account - Use to record debt or expenditures where the source of the funds or expenditure is unspecified. This account type is recorded as a liability.
-
Equity account - Use to record retained earnings and other trust equity. This account type is recorded as an asset.
-
Advance - Use to record an extension of trust funds in the form of a loan to a third party.
-
Expense category - Use to record non-asset objects of trust expenditure, such as legal fees or fees paid to a property management agency.
-
Income category - Use to record payments of funds that a trust receives as income.
-
Other account - Use to record any transaction type.
Automatically-created accounts:
These accounts are created automatically when certain transactions are performed.
-
Asset accounts - When a new trust asset is acquired, Connectworks automatically creates an account corresponding to that asset. Any additional transactions performed on the asset (such as sales or sell-downs, capital additions, or re-valuations are recorded as adjustments to the value of the asset account.
-
Distribution accounts - Every party that is recorded as a beneficiary of a trust is able to be the recipient of distributions. When a particular beneficiary is recorded as the recipient of distribution for the first time, a distribution account corresponding to them will be created automatically. Further distributions to the beneficiary will then be recorded as adjustments to the beneficiary’s distribution account.
Default system accounts
These are accounts that every trust has by default.
-
Suspense account - A trust’s suspense account records the movements of funds that have not been allocated to any manually-created accounts. For more on using the suspense account, read the article here.
-
Gifting account - A trust’s gifting account is used to balance the movements of funds into an asset account, where the asset has been received by the trust as a gift, click here to read the article about gifting.
Creating accounts
In most cases, accounts can be created when recording transactions. Each transaction form requires you to select the accounts involved in the transaction. When recording a transaction, you can create the required account by selecting the Add new account option from the account selection drop-down menu. This allows you to create the type of account required for the transaction:
All types of accounts can also be created separately from the transaction recording process. To do this, click on "I would like to..." and select Add an account:
Editing account details
Once an account has been created, you can edit the account details at any time. To do this:
1. Navigate to the Chart of Accounts tab.
2. Place a tick next to the account name, select the "..." symbol in the slide-out menu and select edit:
